Hazard Assessment Form – Quick Tips
Instructions
Hazards exist in every workplace in many different forms. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) 29 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) 1910.132(d)(1) “The employer shall assess the workplace to determine if hazards are present, or are likely to be present, which necessitate the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).” This is commonly referred to as a PPE hazard assessment.
A PPE hazard assessment can be conducted for an area, a job category or for an individual. Affected employees from each work area being assessed should be involved in the process. You should review the job procedures, potential hazards and the PPE currently in use prior to beginning the assessment. Reports of work-related injuries/illnesses, near misses and other reported safety concerns also provide helpful information.
Print this Hazard Assessment Form and use it as a guide when conducting the walk-through survey. Observe the layout of the work area, operations being performed and any hazards present. This form aligns the body part that could potentially be exposed to a hazard and it is addressed by putting a check mark in either the yes or no box. The person who conducts the hazard assessment survey should identify which area or job classification was reviewed, when the assessment was conducted and finally, signs and dates the form when it’s completed.
Before you complete this Hazard Assessment Form, make sure to review the Guidelines for Selecting Personal Protective Equipment found on the last two pages of this form.
Your PPE program should be periodically reviewed and it should be reviewed anytime there is a change in an existing process or a new process is added to your facility.
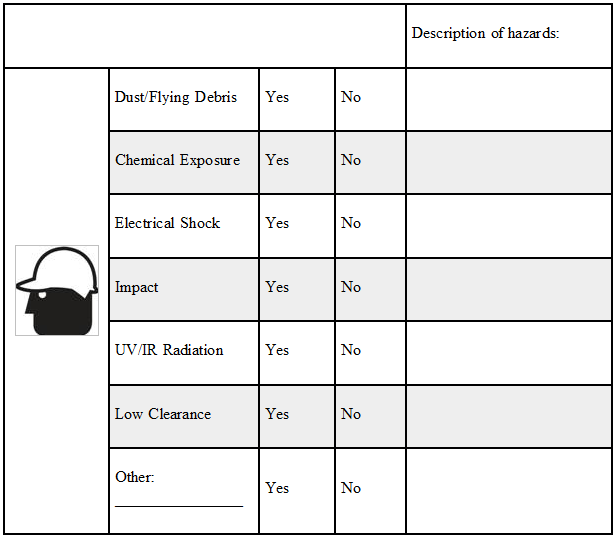
Head Hazards
Tasks that can cause head hazards include, but are not limited to, working below other workers who use tools and materials which could fall, working on energized electrical equipment, welding, working with chemicals and working under machinery or processes which might cause materials or objects to fall.
Check the appropriate box for each hazard:
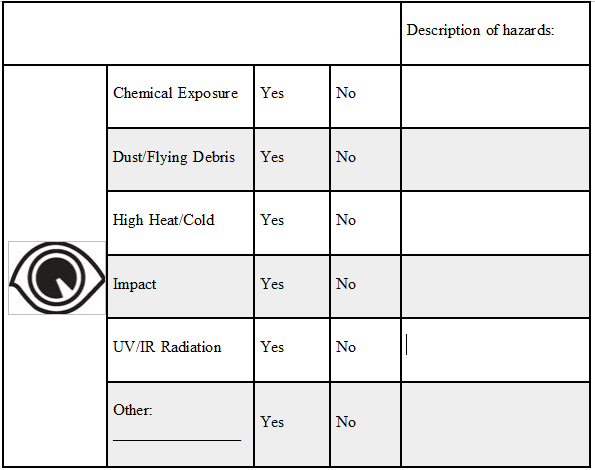
Eye and Face Hazards
Tasks that can cause eye or face hazards include, but are not limited to, working with chemicals, chipping, grinding, furnace operations, sanding, welding, UV radiation and woodworking.
Check the appropriate box for each hazard:
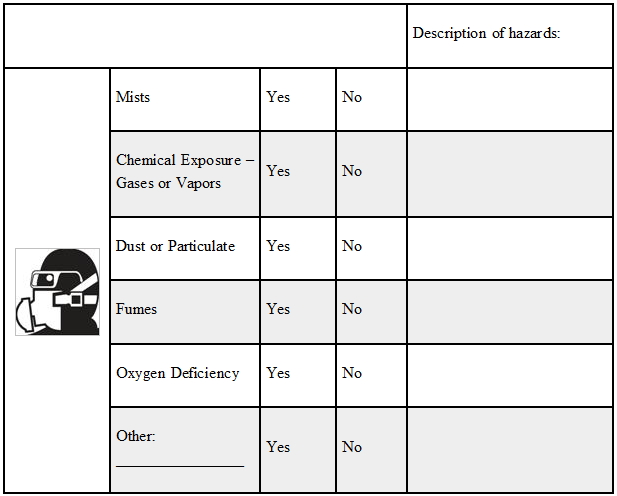
Respiratory Hazards
Tasks that are associated with respiratory hazards include, but are not limited to, welding, grinding spray painting, working in confined spaces, chemical processing and potential exposure to asbestos, lead, silica or other particulate hazards. Exposures to these and other respiratory hazards can make you sick or can be deadly. These hazards come in the form of gases, vapors, dusts, mists, fumes, smoke, sprays and fog.
Check the appropriate box for each hazard:
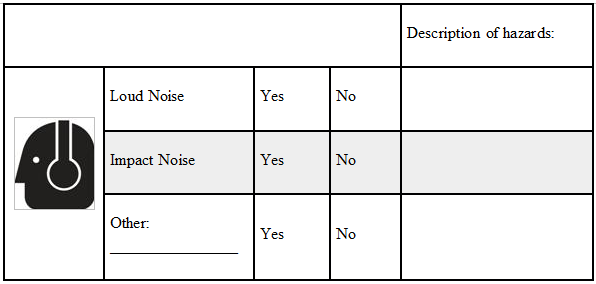
Hearing Hazards
Tasks that can cause hearing hazards include, but are not limited to, working with or around loud machinery or tools in mechanical rooms, machining, grinding, sanding, pneumatic equipment, grounds equipment, generators, chillers, motors, saws, jackhammers or similar equipment.
Check the appropriate box for each hazard:
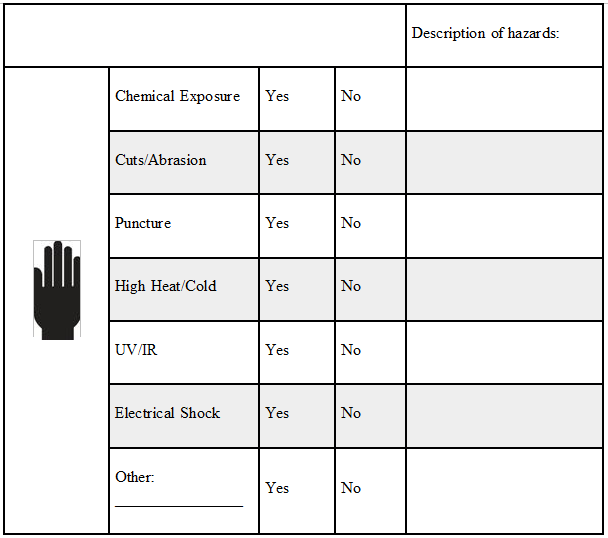
Hand/Arm Hazards
Tasks that can cause hand hazards include, but are not limited to, exposure to cut or abrasion hazards, working with chemicals, working with very hot or cold objects or materials and exposure to sharps.
Check the appropriate box for each hazard:
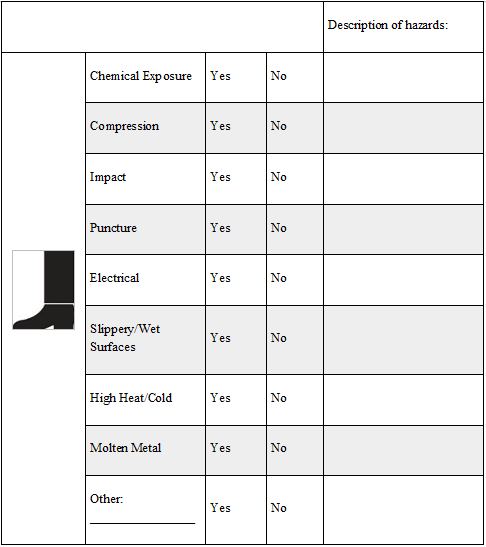
Foot/Leg Hazards
Tasks that can cause foot hazards include, but are not limited to, carrying or handling materials that could be dropped, performing manual material handling, welding, cutting, electrical work and working with chemicals.
Check the appropriate box for each hazard:
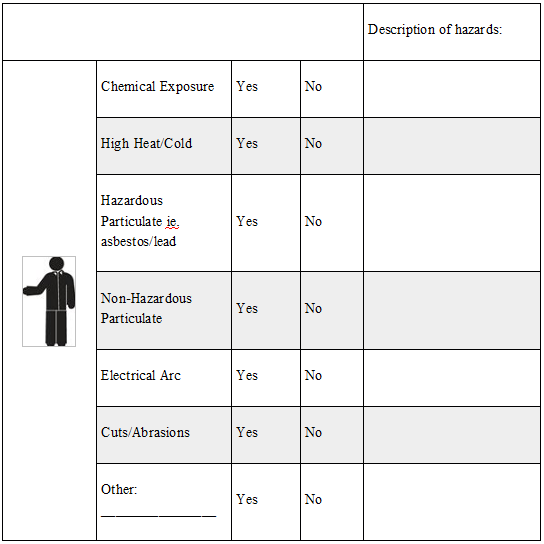
Other Required PPE
Do hazards exist that require PPE for the Body? Chemical exposure, abrasive blasting, welding, cutting or brazing, chipping, sanding or grinding, electrical arc hazards and bloodborne pathogens are some examples of hazards that can affect the body. These hazards may require PPE to protect clothing and skin from harm or contamination.
Check the appropriate box for each hazard:
Company Name: __________________________________________________
Location: _________________________________________
On the following date(s), _________________________, a comprehensive assessment of workplace hazards requiring the use of Personal Protective Equipment, as required by 29 CFR 1910.132 (d) of the OSHA General Industry Standards, was conducted at this facility to the best of my knowledge based on the current conditions.
Printed Name: _______________________________ Job Title: _________________________________
Signature: _____________________________________ Date: ______________________________
Guidelines for Selecting Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Work-practice controls should be implemented before utilizing PPE to control worker exposures to hazards in the workplace. This is based on OSHA’s hierarchy of controls which includes: engineering controls, administrative controls and work-practice controls. PPE alone should not be relied on to provide protection against hazards. PPE should be used in conjunction with engineering controls and administrative controls. PPE is viewed as the last line of defense.
Factors to consider when selecting PPE:
- Familiarize yourself with the potential hazards in the area and the types of PPE that are available
- Consider the hazards associated with the environment (impact velocities, masses, projectable shape, radiation intensities, etc.)
- Consider the following basic hazard categories:
- Impact (falling/flying objects)
- Penetration (sharp objects piercing foot/hand)
- Compression (roll‐over or pinching objects)
- Chemical exposure (inhalation, ingestion, skin contact, eye contact or injection)
- Temperature extremes (heat/cold)
- Dust/flying debris (grinding, chipping, sanding, etc.)
- Radiation (non‐ionizing: UV/IR/light, welding, brazing, cutting, furnaces, etc.)
- Noise (mechanical rooms, machines, jackhammers, etc.)
- Electrical (shock, short circuit, arcing, static)
- Select PPE that ensures a greater level of protection than the minimum required to protect workers from the hazards
- Fit the worker with the PPE and give instructions on its use and care. It is very important that workers be made aware of all warning labels and limitations of their PPE
Based on the hazard assessment for ______________________________ (Job Classification), the following PPE is required:
Sources
OSHA Personal Protective Equipment Booklet (Rev. 5/2015)
The information contained in this article is intended for general information purposes only and is based on information available as of the initial date of publication. No representation is made that the information or references are complete or remain current. This article is not a substitute for review of current applicable government regulations, industry standards, or other standards specific to your business and/or activities and should not be construed as legal advice or opinion. Readers with specific questions should refer to the applicable standards or consult with an attorney.
Source: Grainger Know How – https://www.grainger.com/know-how